Environmental degradation takes many forms and is one of the largest crises we face as a planet. If things don't change soon, the outlook is bleak.
There is no denying the significant (and often negative) impact humans have had on the natural environment. The term environmental degradation refers to how the planet’s natural resources are compromised through natural and human-accelerated activity.
According to many environmental organizations, environmental degradation is one of the most challenging issues we are facing. We have one planet to work with, and if we damage it beyond repair, humankind may bring about its own extinction. It’s important to understand the causes of this phenomenon and the effects it can have on the planet so we can begin to understand how to come up with solutions.
What Causes Environmental Degradation?



(Foto: CC0 Public Domain / Unsplash / Matt Palmer )
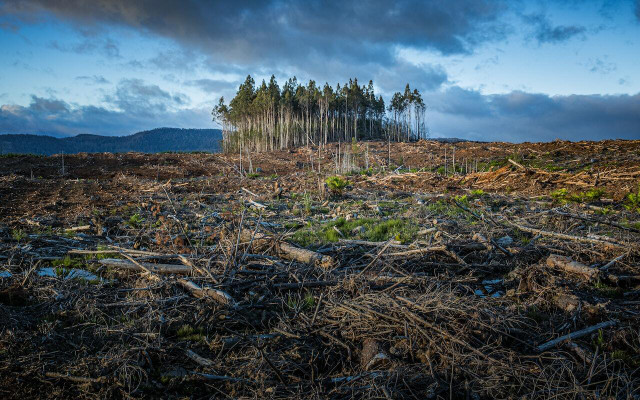
The planet is full of diverse climates, ecosystems, and topographical features, so environmental degradation is a multifaceted issue. There is no single cause, but rather a collection of issues occurring around the globe that contribute to this vast problem.
- Intensive Agricultural Practices: The conversion of forests and grasslands into croplands significantly contributes to environmental degradation. Entire ecosystems are destroyed when land is cleared, and problematic farming practices, including factory farming and significant pesticide and fertilizer use, also have knock-on effects.
- Landfills: Landfills are a serious problem and a huge contributor to many environmental issues. They pollute the land, water, and air as the garbage breaks down. This has negative impacts on surrounding wildlife, habitats, and ecosystems.
- Deforestation: The process of cutting down trees for farming, construction, housing, mining, or other economic purposes plays a large role in environmental degradation. It depreciates the natural environment and displaces wildlife in the surrounding areas, as well as impacts weather patterns.
- Overpopulation: The population of the planet has skyrocketed over the last hundred years, going from approximately 1.9 million to recently surpassing the 8 billion mark. This places a lot of pressure on natural resources and leads to overexploitation. More people means more pollution.
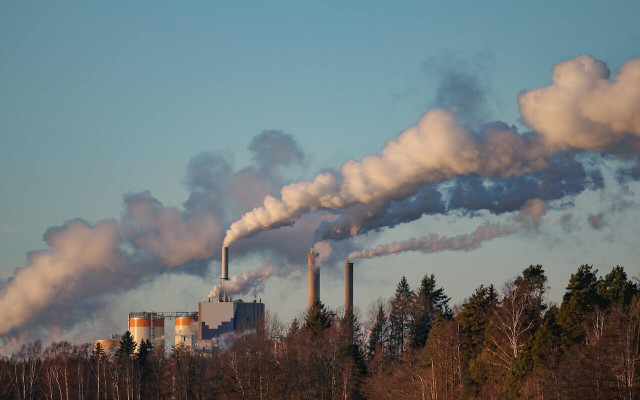
- Environmental Pollution: Many natural environments around the globe have been harmed by pollution from fossil fuel combustions, commercial and industrial waste, along with household chemicals and plastics.
- Natural Causes: Natural causes are also contributors to environmental degradation. Occurrences such as wildfires, hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, landslides, tsunamis, and earthquakes can also alter and destroy landscapes.
Three Main Categories & Examples



(Foto: CC0 Public Domain / Unsplash / Daniel Moqvist)
Environmental degradation can be broken down into three main categories, though several subcategories also exist. Two other factors that also contribute include light pollution and noise pollution, as both have ramifications on the natural environment.
Land and Soil Degradation
Land and soil degradation is one of the most visible forms of environmental damage. Soil quality can be altered by poor farming practices, landfill leakage, and excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. Other harmful human activities that contribute to land and soil degradation include deforestation, mining, and fossil fuel extraction.
Water Degradation
Most of us are aware that plastic pollution in oceans exists, but that isn’t the only thing that contributes to water degradation. One of the most detrimental forms of pollution in all of our waterways is microplastics. There are also cases of oil spills, illegal dumping, and disposal of industrial waste into rivers and lakes, all of which contribute to dead zones in our oceans. Groundwater can also be affected when man-made products (such as road salts, gas, oil, and chemicals) seep into the earth and infiltrate groundwater supplies.
Atmospheric Degradation
Atmospheric degradation isn’t always visibly apparent, which can make it one of the more easily forgettable forms of environmental degradation. Unfortunately, it doesn’t make it any less toxic. The quality of air is impacted by particle pollution and carbon emissions, which have also contributed to the depletion of the ozone layer. Human activities that have accelerated atmospheric degradation include transport and factory emissions, landfills, and the burning of waste.
What Are The Knock-On Effects?


(Foto: CC0 Public Domain / Unsplash / Brian McGowan)
It’s easy to focus on the causes, but the problem becomes even more clear when you look at the knock-on effects of environmental degradation. We’ve chosen to highlight a few of them here, though there are so many more than the ones we’ve listed.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Continued destruction of natural habitats has significantly contributed to the mass extinction of species across the globe. The number of endangered species is on the rise, and we need to employ significant conservation efforts if we want this to change.
- Human Health: Human health is absolutely influenced by environmental degradation. Water pollution is responsible for nearly 830,000 deaths per year, while air pollution is said to contribute to approximately seven million premature deaths per year. Biomagnification also poses a threat to human health.
- Atmospheric Changes: Pollution affects the natural balance of the planet, which contributes to global warming and climate change. This increases the risk of natural disasters and ozone depletion, which can also affect human health through crop failures and lack of access to necessary resources.
- Environmental Refugees: There has been an increase in the number of climate migrants who are forced to leave their homes due to changes in their local or regional environment that compromises their well-being and livelihoods. Increased drought, desertification, and rising sea levels are just some of the reasons people need to leave their homes.
Read more:
- Environmental Activism: How To Get Involved in 2022
- Life Without Plastic: Easy Tips for Everyone
- What Is a Bioregion And Which Ones Are There?
Do you like this post?








