Knowing the difference between high and low FODMAP fruits will help you maintain a balanced diet while identifying which foods might trigger digestive discomfort and IBS symptoms.
The interest in low FODMAP fruits and other foods for the management of gut disturbances and disorders has been steadily increasing over the years. Many people suffer digestive issues and debilitating issues – like bloating, constipation and diarrhea – when they eat certain foods. Known as triggers, these foods are often nutritious in other ways and are important part of a balanced diet. So before attempting a low FODMAP diet, find out what exactly it involves and which healthy fruits you can eat safely without triggering symptoms.
What Exactly Is a FODMAP Diet?
(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / hagelund)
A low FODMAP diet restricts certain carbohydrates, but it is not your typical low-carb diet. The FODMAP acronym stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols – more commonly known as fermentable carbohydrates. These sugars are poorly absorbed in the small intestine of some people and pass through to the large bowel, where they are fermented by bacteria.
Gas is subsequently produced by the bacteria, causing bloating, flatulence and crampy pain. This can also cause water to move into and out of the colon, resulting in diarrhea, constipation or a combination of both. People with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) in particular are finding relief from following a low FODMAP diet.
The Low FODMAP Diet



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / mohamed_hassan)
Described as a three-step diet by John Hopkins Medicine, the low FODMAP diet was originally developed by a research team at Monash University in Melbourne, Australia. It involves eliminating high FODMAP foods and then slowly reintroducing them to identify triggers. The third stage involves a return to a balanced and varied diet that promotes gut health, microbial diversity and the absence of symptoms.
Fruit is a rich source of essential nutrients but also contains the monosaccharide fructose and the polyol sorbitol, among other compounds that can contribute to gut disturbances. It is important that you eat a varied and balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables to maintain adequate nutrition levels. Unfortunately, many of our plant-based nutrient bombs are high in FODMAPs. Therefore, knowing which fruits are safe will help you to stay nourished while identifying potential triggers of your gut disturbances. High FODMAP fruits to be avoided include:
- Apples
- Pears
- Mangos
- cherries
- Pears
- Watermelon
- Dried fruit
- Blackberries
- Plums
- Cherries
1. Blueberries



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / congerdesign)
Blueberries are a nutritious low FODMAP fruit that do not contain high amounts of fructose – which can be difficult to digest. Limit your portion size to less than twenty and continue to enjoy health benefits – like a reduced risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease, as well as improved weight maintenance and neuro-protection.
2. Unripe Bananas



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / Ninifee)
Fructans are oligosaccharides and a source of dietary fiber. Farmers may also be selectively breeding varieties of crops with a higher fructan content because they tend to be more resilient to pests and diseases. Ripe bananas are full of fructans but unripe bananas contain very few – so go green and safely enjoy the nutritious contents of this tasty superfood.
3. Strawberries



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / JesusLeal)
Monash University recently retested strawberries and recommend a safe portion size of five medium sized berries while following a low FODMAP diet. These low FODMAP fruits have been linked to many health benefits thanks to the bioactive compounds and plant chemicals they contain. Studies show that strawberries might play a role in:
- Reducing inflammation
- Weight management
- Reducing the risk of heart disease
- Protecting against cancer
4. Kiwi



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / PhotoMIX-Company)
Kiwi has been shown to improve gut function in IBS victims suffering from constipation and is on the low FODMAP list. It also boasts a low glycemic index – meaning it does not cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. Research has shown that eating two kiwis resulted in no malabsorption issues and they are considered safe low FODMAP fruits during the elimination phase of the diet.
5. Oranges



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / pixel2013)
Oranges are a zesty low FODMAP fruit, but you should avoid concentrated forms in juice and stick to a small- to medium-sized whole orange. Oranges are an excellent source of vitamin C and potassium, among other nutritious compounds – like fiber – that benefit health. Don’t miss out and get your complete recommended daily dose of vitamin C from just one portion.
6. Pineapple
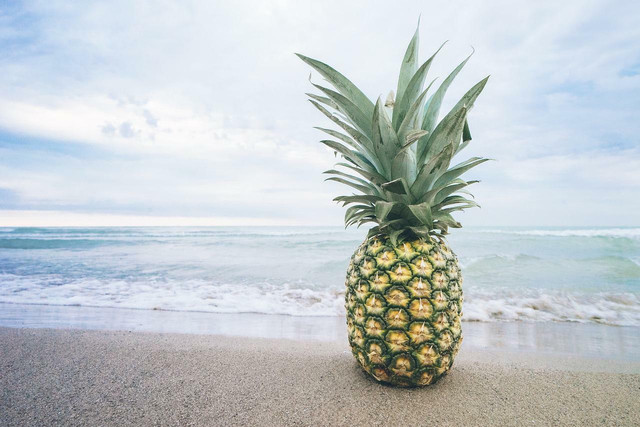



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / Pexels)
One cup of fresh chopped pineapple is considered low FODMAP and will provide you with reasonable amounts of essential nutrients like:
- Fiber
- Vitamin C
- Manganese
- Vitamin B6
- Copper
- Thiamine
This tropical treat contains several bioactive compounds and has been linked to many health benefits. Pineapple also boasts anti-inflammatory properties, so why not give your body a boost?
7. Dried Cranberries



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / Alexey_Hulsov)
Dried cranberries are low FODMAP and you can safely enjoy 1 tablespoon while eliminating higher FODMAP fruits. Monash University has never tested fresh cranberries but do list dried as a safe alternative. Some of the major reported benefits of consuming cranberries include:
- Prevention of urinary tract infections
- Prevention of dental cavities
- Improved heart and gut health
- High content of antioxidants
- Cancer prevention
8. Cantaloupe



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / PatriciaMaine)
Cantaloupe has a generous low FODMAP serving size of 3/4 cup chopped. These low FODMAP fruits have good nutritional properties that studies suggest might benefit human health and allow you to manage chronic diseases. Mix and match your melons and other low FODMAP fruits to ensure you receive all of the essential vitamins and minerals required for optimal health and wellbeing.
9. Honeydew



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / Dennis)
Honeydew melon is a safe low FODMAP fruit at ½ cup per portion. The content of fructans does begin to rise beyond this amount, so be cautious. California produces the majority of honeydew sold in the US, so always try to buy as locally and sustainable as possible. Honeydew is described as the sweetest of all melons and, like cantaloupe, will add a delicious and nutritious boost to brain and body.
Read more:
- Does Fruit Have Protein? 12 High-Protein Fruits
- Orange Juice & Espresso: How to Make the TikTok-Trend
- Quick Fruit Salad Recipe
Do you like this post?






