With all the fad diets and mixed messages on social media, it can be hard to discern which fats are good or bad for you. The term "polyunsaturated" may seem scary and intimidating, but these oils are actually very important to your health.
Unsaturated fats are dietary fat molecules that have double bonds. Those with one double bond are called monounsaturated fats, and those with more than one double bond are called polyunsaturated fats. At room temperature, polyunsaturated fats are usually in liquid form, which is why they are typically referred to as oils. Let’s take a closer look at whether polyunsaturated fats are good or bad.
Polyunsaturated Fat: Good or Bad?

(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / parkstonephotography)
The two types of polyunsaturated fats are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. A healthy diet must include both, as these fatty acids are imperative to brain function and cell growth, and our bodies cannot produce these fats themselves. Compared to saturated fats, polyunsaturated fats are a great alternative because they can reduce levels of cholesterol and risk of heart disease. In fact, high consumption of polyunsaturated fats has been linked to a lower risk of dementia, and can also help improve menstrual pain.
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to benefit mental health by helping fight depression, anxiety, and mental disorders like bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. They also can even improve ADHD symptoms in children, help aid those with metabolic syndrome and reduce vision impairment. Omega-6 fatty acids help reduce risk of diabetes and increase hair growth.
Downsides of Polyunsaturated Fat
Overall, polyunsaturated fats offer many benefits. However, as with anything, they should be consumed in moderation. Polyunsaturated fats, like all fats, are high in calories. They have about nine calories per gram, which is more than two times the amount of calories in carbs and protein. There can also be negative side effects of overconsumption. Consuming too many omega-6 fatty acids, for example, can result in too much inflammation in the body. While some pro-inflammatory ingredients can be helpful in fighting infections and healing wounds, chronic inflammation can contribute to obesity, diabetes and heart disease. A typical US American diet includes plenty of omega-6 oils, and not enough omega-3’s. This can contribute to heart disease, so make sure you pay attention of your ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids.
Polyunsaturated Fats in Fish
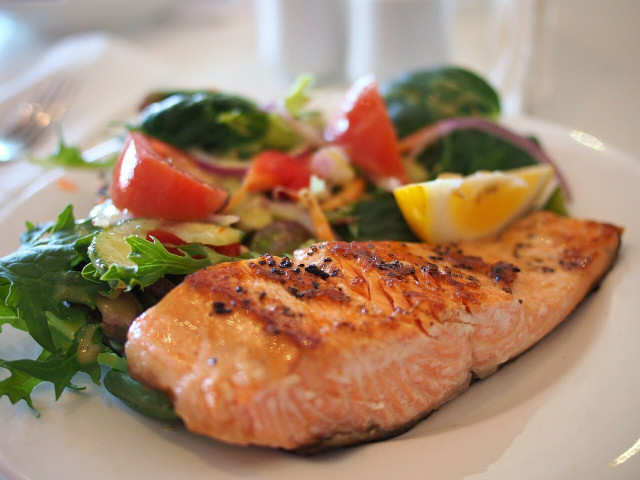
(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / cattalin)
When people think of omega-3 fatty acids, they often think of fish. Salmon is one of the most common sources of omega-3 fatty acids people consume. Other fish which are high in omega-3 include:
- herring
- sardines
- mackerel
- trout
- bass
- shrimp
Due to the fishing industry’s contribution to environmental degradation and plastic pollution in the ocean, you need to be mindful when consuming fish. Commercial fishing is leading to a mass extinction due to overfishing and habitat damage. Farm fisheries are often not any better because they destroy local ecosystems through pesticide and fertilizer waste. Salmon fisheries specifically, rely on smaller, wild caught fish to feed to the salmon – a practice which negatively impacts fish and other wildlife over time. If you do prefer to get your polyunsaturated fats from fish, look to purchase wild salmon from sustainable sources.
Vegan Sources of Polyunsaturated Fats
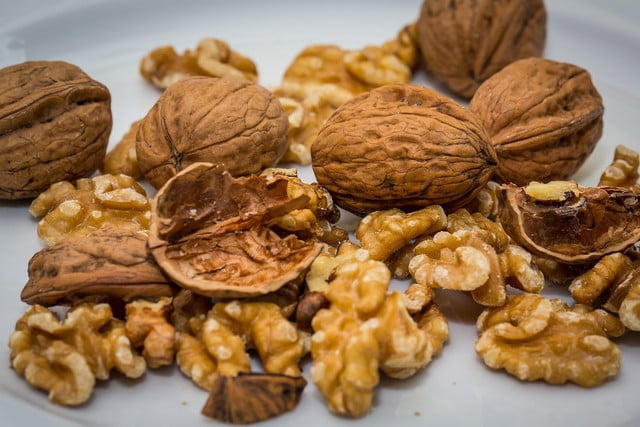



(Foto: CC0 / Pixabay / maxmann)
The good news is that polyunsaturated fats are also found in plant-based oils, seeds and nuts. For omega-3 fatty acids, some plant sources include:
- Pine Nuts
- Walnuts
- Linseed
- Pumpkin Seeds
- Flax Seeds
- Chia Seeds
- Sunflower Seeds
While these vegan sources are not as high in fat as salmon or herring, they are much more sustainable than fish. Plus, it doesn’t take much to reap the benefits. One tablespoon of chia seeds or just three walnuts is enough to hit your daily intake of omega-3 fatty acids. You can easily add either of those to your overnight oats. Or, have fun making roasted pumpkin seeds and snack on those.
For omega-6 fatty acids, most plant-based oils are a great source. Here are some ideas:
- Safflower Oil
- Grapeseed Oil
- Avocado Oil
- Flaxseed Oil
- Sunflower Oil
- Soybean oil
- Tofu
- Peanut Butter
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Walnuts
All of these are easy to incorporate in your diet as cooking oils, snacks or main ingredients. For the plant oils, make sure you store them in a cool, dark place before opening. After you open them, they should be placed in the refrigerator. When cooking with polyunsaturated oils, keep in mind that they have a lower smoke point. When the oil smokes, the fat breaks down and can produce harmful substances like carcinogens. So make sure to use low to medium heat when cooking with these oils
Read more:
- Swai Fish: 5 Reasons Not to Eat Pangasius
- Chia Seeds vs. Flax Seeds: What’s the Difference and Which is Better?
- 8 Things You Can Do to Save the Ocean
Important Information regarding Health-related Topics.
** Links to retailers marked with ** or underlined orange are partially partner links: If you buy here, you actively support Utopia.org, because we will receive a small part of the sales proceeds. More info.Do you like this post?









